
with launch James Webb Space Telescopea Milky Way, The galaxy in which our planet is located, is experiencing an even more intense time of scientific exploration and possible discoveries.
The researchers expected that the most powerful observatory (Expensive) Already sent to space bring more answers Concrete facts about the mysteries behind the earth. thinking about it, tilt I made a list of everything you need to know about our “little corner” of the universe.
What is the Milky Way?
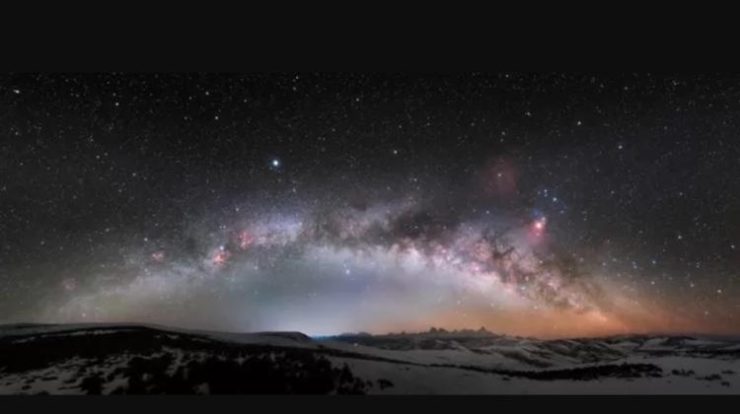
Let’s start with the basics: The Milky Way is a system of stars, dust, and gas bound together by the force of gravity. It is a spiral galaxy estimated to be 13.6 billion years old.
The Milky Way’s disk – the surrounding structure responsible for giving it this spiral shape – is about 100,000 light-years in diameter, but only 1,000 light-years thick (remember that each light-year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers).
And where are we from this?
all of us Solar System It is located in the galaxy and revolves around its center, in the same way that the Earth revolves around the sun. This entire episode takes 250 million years to complete.
In any case, our planet is reasonably far from the center of the galaxy: if we want to compare it with a city, then Earth would be located in the suburbs, at a distance of 25 thousand-30 thousand light-years from the center.
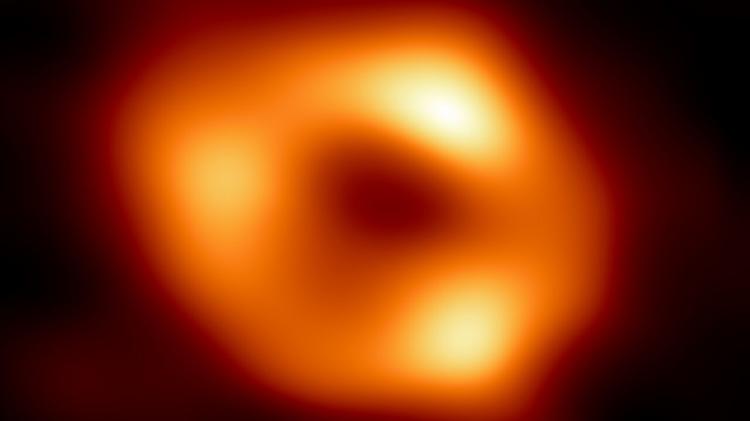
It is good that we are not in this position because there is a file Black hole super huge Sagittarius A* (pronounced “A-star”), which has a mass approximately 4 million times the mass of the Sun.
In 2022 for the first time Humanity has managed to produce a picture of this black holethat feed on stellar matter.
If the record seems a little “blurred”, it’s because, in fact, it was taken through thousands of different shots, with different directions of black hole motion. At the time, scientists commented that it was like filming “a dog trying to catch its tail.”
Why was the Milky Way called that name?
If the night is clear and we are in a place without a lot of light and pollution (ie away from big cities), it is possible to look up at the sky and see a few glimpses of the glow of the galaxy, which seems to be long. White line.
According to Greek mythology, this glow in the sky would be because the goddess Hera was going to spill milk on it. Hence the name “Milky Way”, which would be a kind of “milk path”.
It is a poetic way of invoking this effect that appears in heaven, immortalized in poems and songs ranging from Legião Urbana to Dua Lipa.
However, according to information from the Space website, this will not be the only name humans give the galaxy. In China, some know it as the “Silver River”, while in the Kalahari Desert, in South Africa, its name is the “backbone of the night”.
What galaxies are our neighbors?
There are two large satellite galaxies near the Milky Way, known as the Magellanic Clouds, that can only be seen from Earth’s southern hemisphere. They are called “dwarf galaxies” for their lineage – their number of stars is only about one in a hundred of the large galaxies.
For a long time, astronomers wondered how they could survive and still form stars as they orbit each other and are pulled toward our galaxy.
In this case, one would expect that they would not have more gas to generate a lot of stellar material.
But recent observations from the Hubble telescope show that the answer to this mystery may lie in the fact that the Magellanic Clouds are surrounded by a kind of protective shield of hot, supercharged gas called a “crown.”
This halo surrounds dwarf galaxies and prevents their gases from deflecting by the Milky Way, giving them the conditions to continue forming stars.
Another important neighbor is the Andromeda galaxy, against which the Milky Way is traveling at a speed of 400,000 km / h. But don’t worry: Scientists estimate that a galaxy collision won’t happen in 4 billion years.
* With information from the space website

“Web geek. Wannabe thinker. Reader. Freelance travel evangelist. Pop culture aficionado. Certified music scholar.”




:strip_icc()/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2024/N/q/BkpyYyS06rBAgGeXtYow/o-robo-perseverance-da-nasa-esta-coletando-amostras-da-cratera-jezero-em-marte.-o-plano-e-enviar-essas-amostras-para-serem-estudadas-na-terra.jpg)


:strip_icc()/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2024/Q/F/WBipAXRwqO8rdLAQtPnA/aranhas-esa.png)