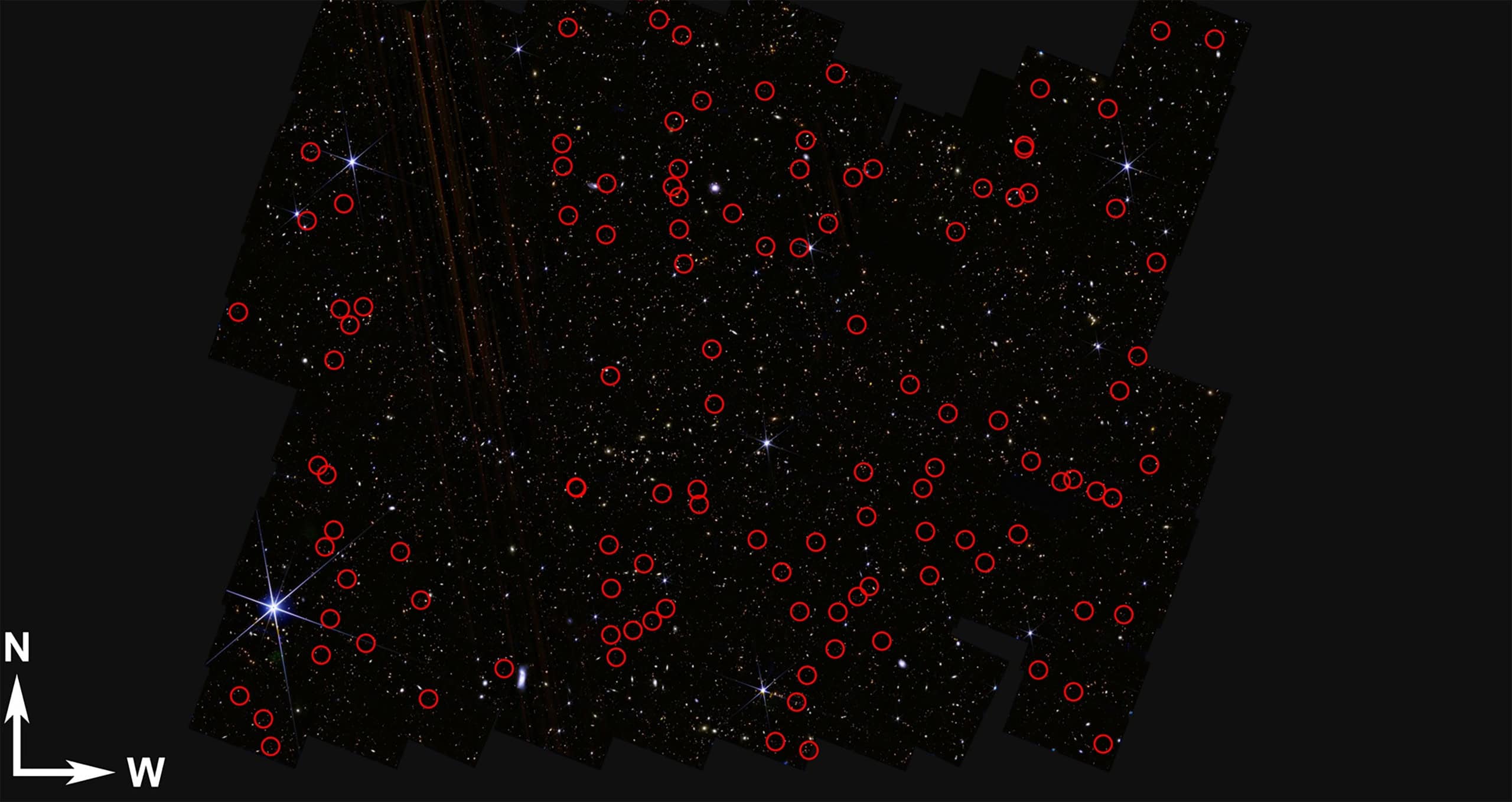
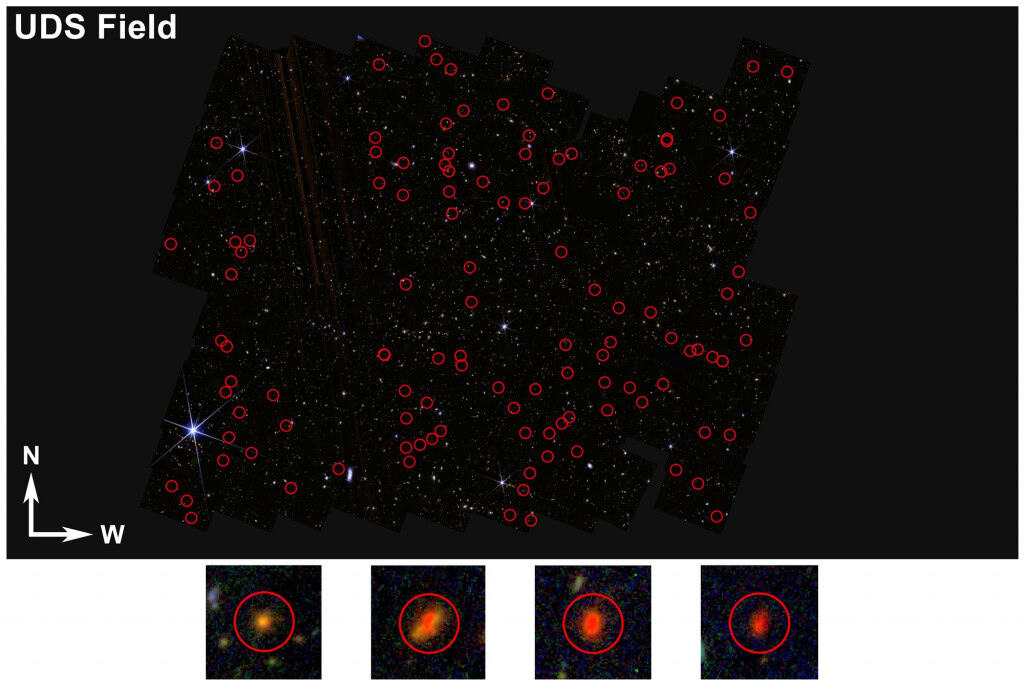
Using the deep field images of the JWST Telescope from the JWST, researchers at Missouri University have identified 300 extensive being exceptionally wonderful in the primitive universe. The discovery was published in the scientific magazine Astronomical physical magazine.
Although it may be galaxies, scientists are not sure yet. The galaxies that were formed shortly after the big explosion should be weak and small, limited from the speed of the formation of stars. However, these organisms shine much more than the current models predicted.
short:
- James Web telescope data revealed 300 wonderful being from the beginning of the universe;
- They can be galaxies, but current models do not explain this extreme brilliance;
- “Make up“The study has concluded for a longer period of time than expected distances;
- Infrared analyzes revealed age, pasta and turning into red things;
- Future spectral notes can confirm that they are truly primitive galaxies.
Huging Yan, the study company, said in a communication.
The infrared display of James Web was necessary for discoveries
To locate their location, the team used a technique “”Make up“Who determines the objects that appear in the red light, but add them in blue. This indicates that they are very far, as they show the universe because it was more than 13 billion years.
The distance was estimated by brightness analysis in different wavelengths, detection of age, pasta and deviation to red. Infrared JWST tools were necessary because they were able to detect light travel for billions of light years.

“While the light of these galaxies travels through space, it extends from visible light to infrared,” Yan explained. This elongation, called the deviation, refers to red, to the distance and the beginning of the universe.
The next step for the team is to make spectral notes focus on the brightest things. Emphasizing that it is rudimentary galaxies will help to understand how the first cosmic structures have formed and developed, adding to the revolutionary discoveries of JWST since 2022.
Read more:
The lens of gravity “Grape Cony” reveals at the beginning of the universe
Another discovery of the most modern space observatory of all ages showed a galaxy at the beginning of the universe in an unusual format.
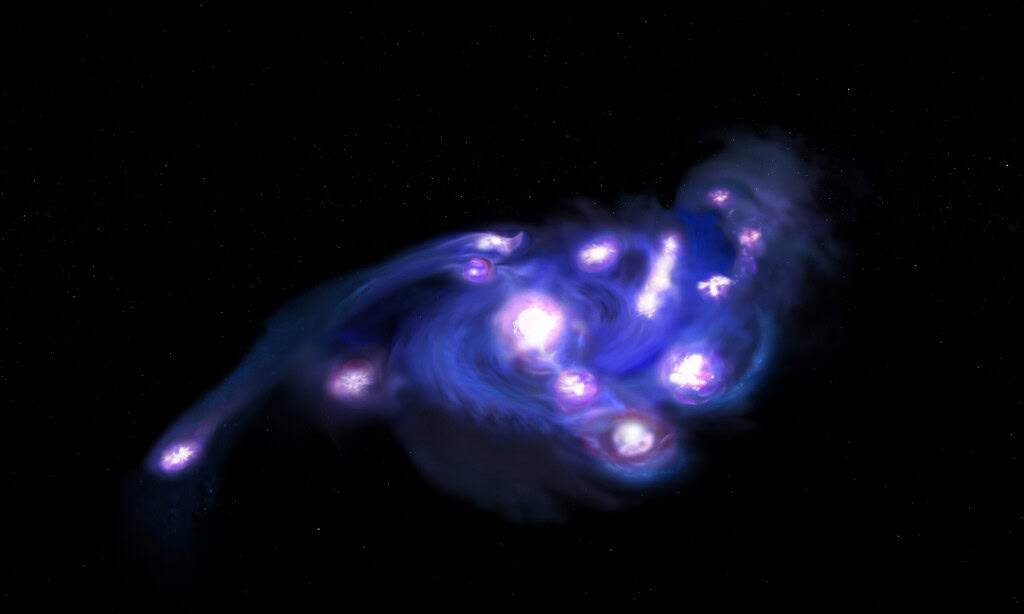

A group of data from JWST and ATACAMA, which allowed a large sublegreter (ALMA), a network of Radiolscopes in Chile, to find researchers to find a galaxy with about 15 combined groups of stars, which appeared after only 930 million years of Big Bang.
The arrangement of these groups as a kind of grapes gave the name “cosmic grapes” to the galaxy. Learn more details here.